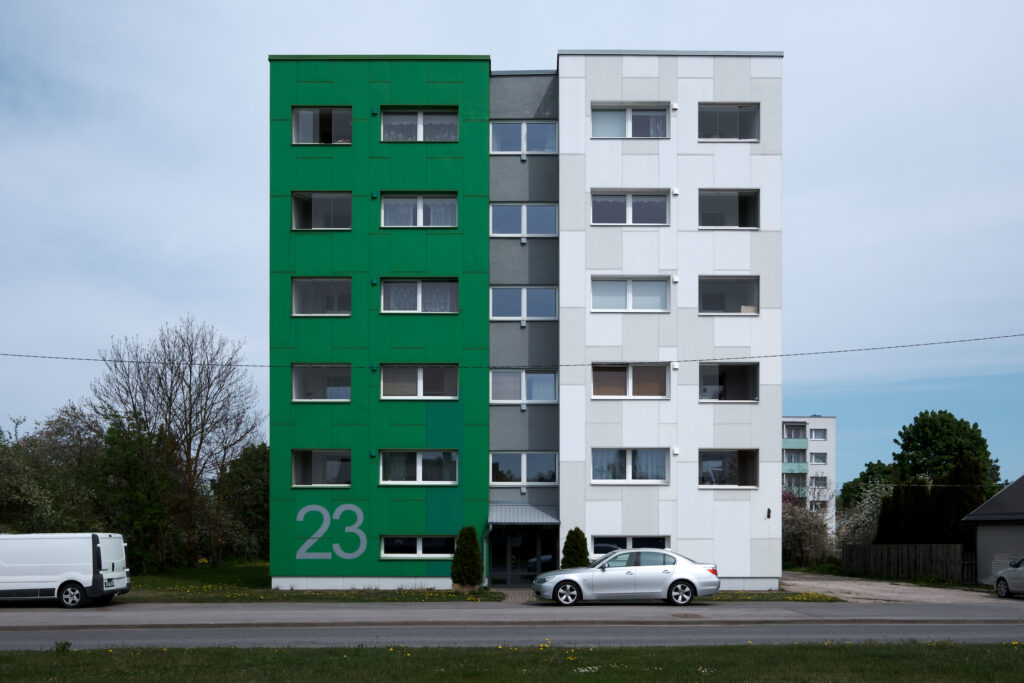
Improving the architectural quality of the existing housing stock requires integrating engineering solutions with architectural decisions. In the ongoing renovation marathon, it is important to discuss what kind of added value could be drawn from the existing to unleash the full spatial potential of renovation and to create good user-friendly spaces, writes Diana Drobot.
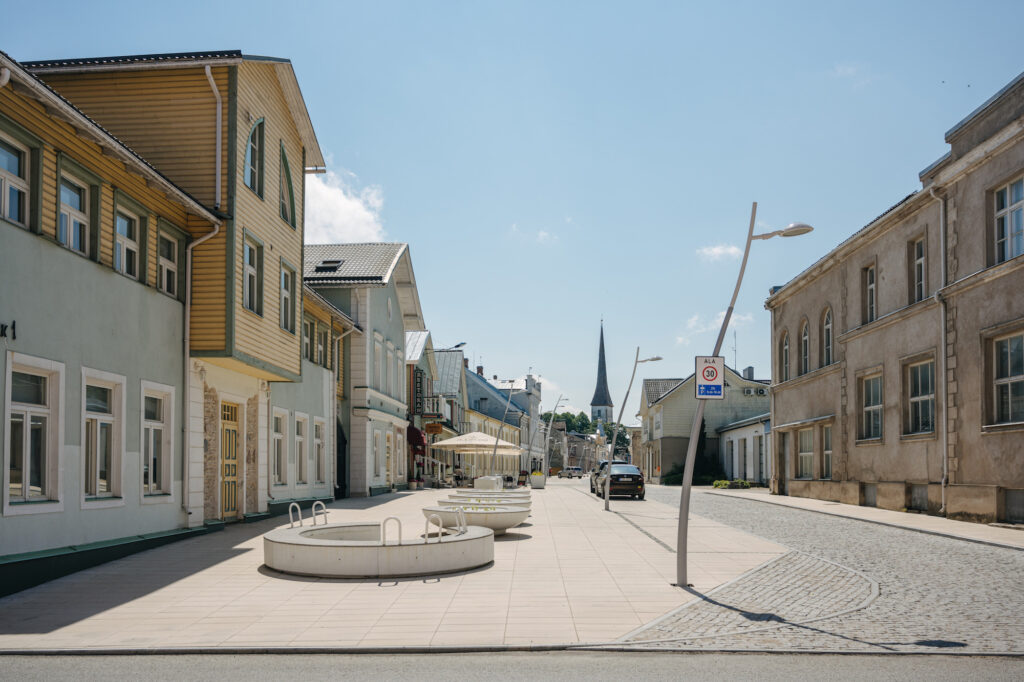
In the course of the programme ‘Great Public Spaces’ dedicated to the 100th anniversary of the Republic of Estonia, the historic street was reconstructed as a contemporary pedestrian-friendly main street. The light monochrome hues of the design create a museum-like exposition complemented with seats, planting, lamps and signage engraved in the pavement and providing information on particular buildings, architectural and landscape objects as well as the town in general.
In the last few years, several public buildings with unexpected combinations of functions have been built in Estonia due to practical reasons, and soon, a series of state houses combining a kaleidoscopic array of institutions in smaller towns will follow. How do these public buildings reflect our present times, and how should they?
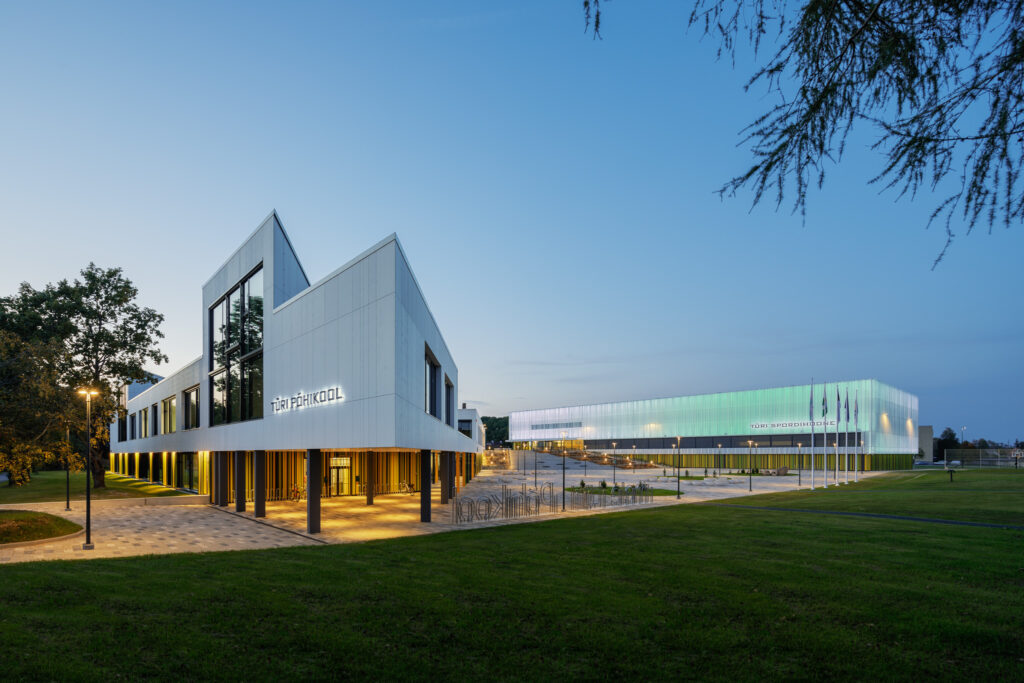
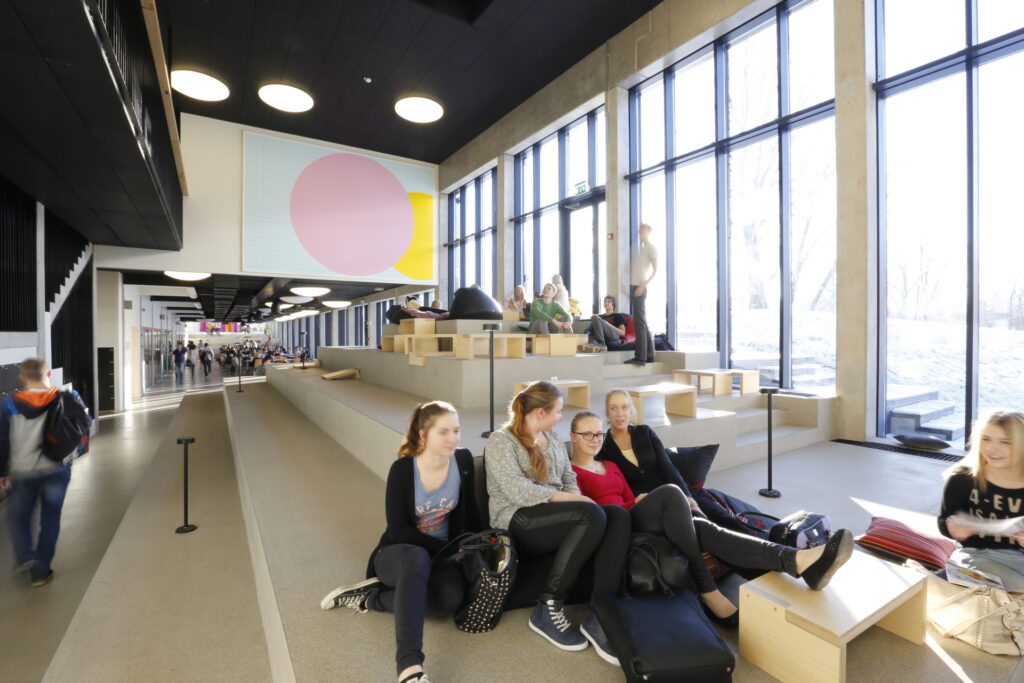
Türi Middle School is a well-executed example of a contemporary school—breaking preconceptions about the organisation of space, encouraging new practices that involve alterations by the users, and offering spatial solutions for socialising as well as withdrawing.
Over the course of the past thirty years, designing school spaces has migrated from being a marginally positioned subject matter to the centre of focus in the field of architecture, supported by scientific studies and continual research and development. The spaces for learning have acquired a new image and meaning.