SPATIAL DESIGN
The most important question regarding the future Tallinn-Helsinki tunnel is no longer if, but how. What kind of unified twin city will Tallinn and Helsinki become thanks to this fast link? This requires foresight and awareness from officials, professionals and politicians.
Professional modern urban management and urban planning mean that urban mobility is developed fully by investing in public transport, along with guiding businesses and residential areas, so that different aspects of urban life support one another
In 2007, the city council again approved the concept “Opening Tallinn to the Sea” with one of its aims including a populated urban space. The simultaneous activities – seaside arterial roads and the wire fences obstructing the sea views and the use of the coast, however, were entirely contrary
This article was born out of concern for the future of our cities, especially Tallinn. It appears to me, as an outside observer, that many large-scale projects in the capital are carried out without any consideration for an overall strategic vision for the city. Although some of the blame can also be placed on the lack of a strong and clear strategic vision for Tallinn, of late, notable progress has recently been made to remedy this situation.
The decisions regarding built environment and living environment have a highly extensive and long-term effect and they are often accompanied also by considerable expenses. Therefore, it is important to increase assurance that the choices made are at a high level and in keeping with the long-term goals.
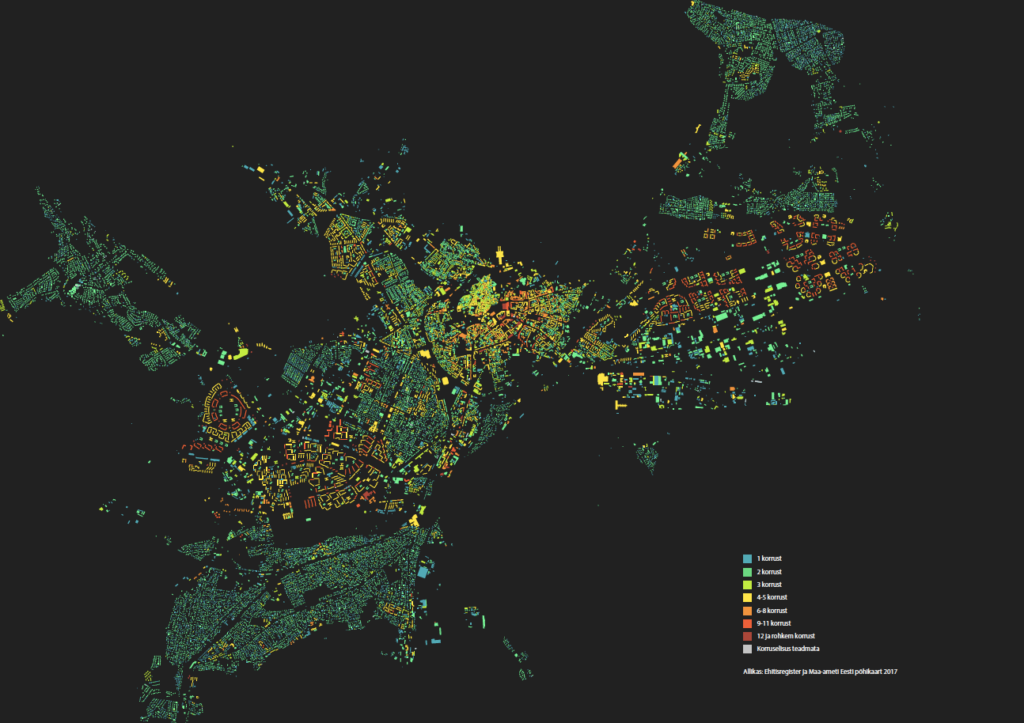
A Research Study on Urban Planning in Tallinn at the Faculty of Architecture of the Estonian Academy of Arts
How to plan and design the city and public space in a situation where every owner of even a tiniest land parcel has its own interests and every public authority or private company has its own needs? How can it be done if every city department has its own concept of urban planning, if architecture and engineering firms expend all their efforts simply keeping their head above water?
It was not easy to aim for a better public space and more human-friendly and diverse street space. Creating an aesthetic city space and a functioning whole was an even more elusive task. It was difficult to explain to the mayor back then what I meant by social space. This combination of words probably gave him a different kind of idea, since the Social Democrats were still in opposition back then. And because all of these ideas were from the point of view of those who actually use urban space (in other words those who don't use cars), many thought they would inhibit progress.
There was a saying in Soviet times that where the railway begins, common sense ends. Looking at the development of infrastructure projects and their particular tendency to become encapsulated in a highly detailed jungle of pipes and wires before much more important issues are resolved, this saying should be paraphrased today as: “Where the designing of infrastructure begins, architecture ends.”
A thoughtfully prepared comprehensive plan acts as a basis for spatial planning decisions, but it is not a substitute for on-site expertise – each local government needs a planning specialist.
Postitused otsas
ARCHITECTURE AWARDS