RUUMILOOME
Contradictions of spatial planning are caused by the time required to process comprehensive and detailed plans as well as (spatial) gap between the two. How to better make sense of planning processes and to alleviate rigidity of the aforementioned?
If there is any feeling of blandness, or risk aversion, or scant sense of place, it is not due to insufficient bike lanes or pedestrian squares, but rather because the larger questions of what is produced and who gets to have how much have already been decided.
Living close to water is good for our health: it reduces the risk of premature death, obesity, and has a generally restorative effect on people’s mental and physical health. 1 In the city, water is often so near, yet so far. Did you know there are more canals in Birmingham than there are in Venice, but people have been separated from the water by bad urban space? Tallinn has a long coastline but there are very few places in the centre where you can access the sea at all.
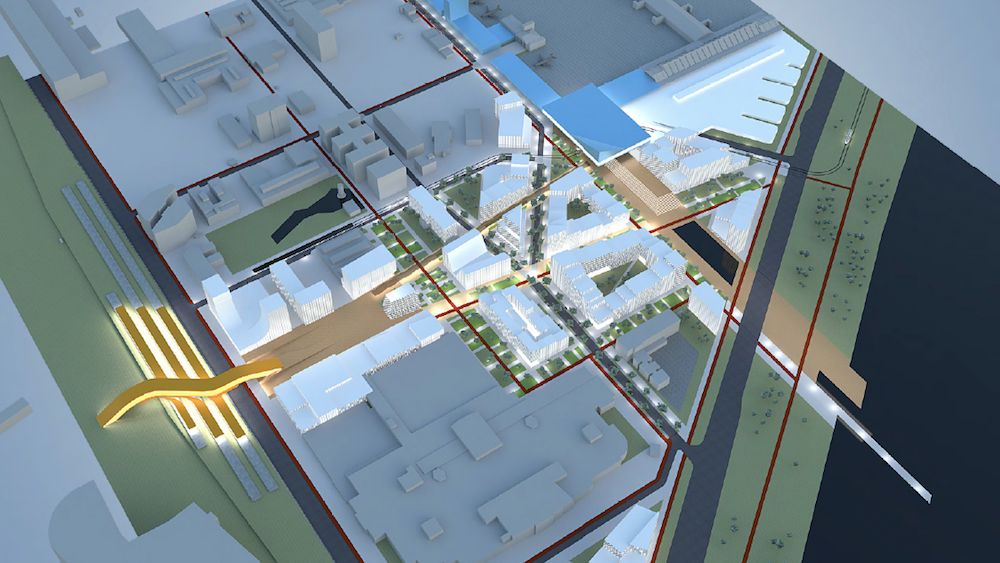
What kinds of forces bear upon the process of creating a new urban area today? What urban development questions do we already have a grip on? What issues are we still grappling with and how? Indrek Allmann recounts the journey toward climate-neutral Paljassaare.
In the last five years, one hot topic for experts in the field of green transition, which has been cropping up at international conferences as well as on the desks of pertinent officials, is the handling of spatial heritage.
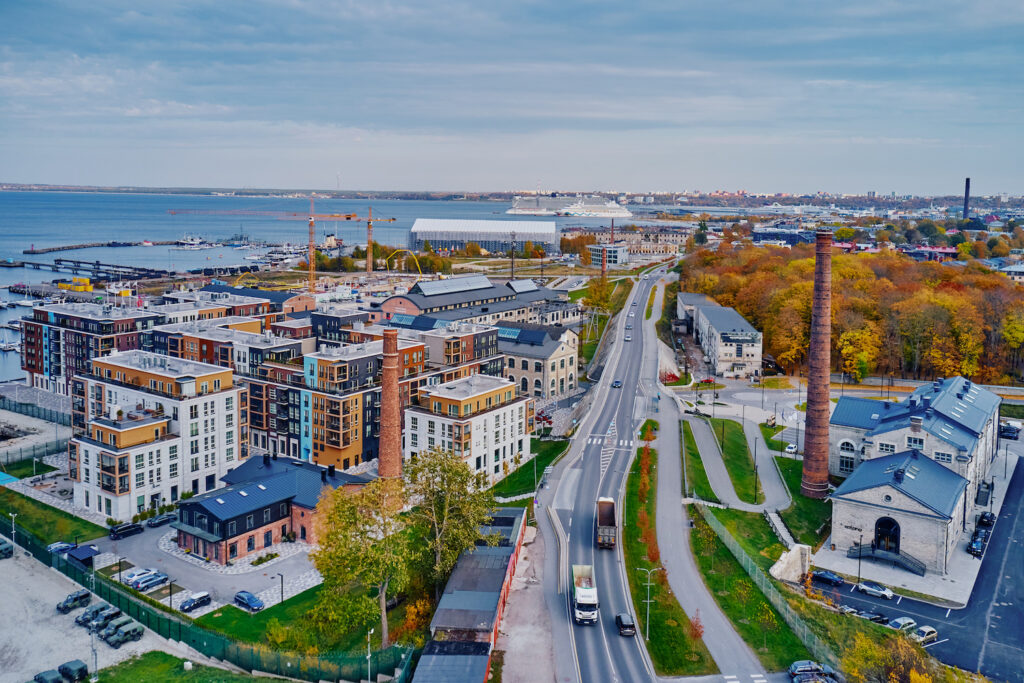
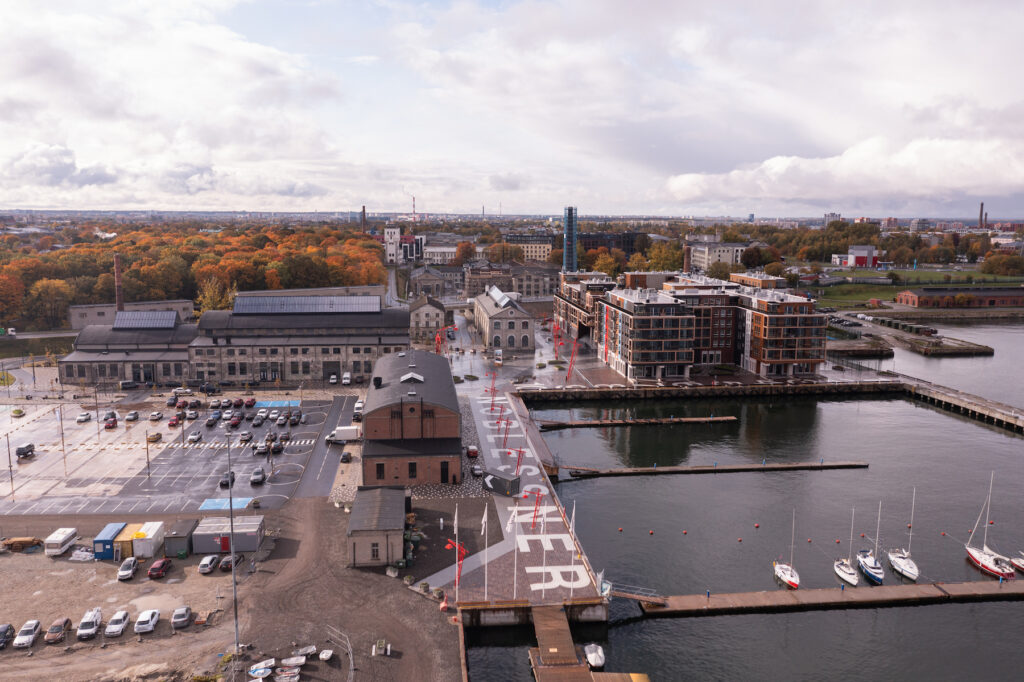
After the slow-burning and partly contestable success stories of Rotermann Quarter and Telliskivi Creative City, the eyes of Tallinners interested in urban design or just longing for a better urban space turned to Noblessner—the privately developed waterfront set to become one of the first chapters on the road to open the coastal areas of Tallinn to its citizens. Though far from complete, the lively quarter already offers a chance for a status report and an insight into the entrenchment of certain spatio-social tendencies in the Estonian real estate landscape.
Andres Sevtsuk is a Professor of Urban Science and Planning at the Department of Urban Studies and Planning at MIT, where he also leads the City Form Lab. Maroš Krivý is a professor of Urban Studies at the Estonian Academy of Arts.They shared their insights on current state and challenges of Estonian architecture.
Since 1994, the architectural review MAJA has been the key platform for promoting and reflecting on Estonian architecture. On the occasion of the 100th issue, all former editors-in-chief – Leele Välja, Piret Lindpere, Triin Ojari, Katrin Koov and Kaja Pae – came together to discuss their working principles and the changes the journal has undergone in the past twenty-five years. Interviewed by Andres Kurg.
What are the advantages and pull factors of rural areas?
Any apartment complex can become a community house if its inhabitants are so in sync that while they need to meet up (cooperative activities) they also want to come together.
Postitused otsas