Editor’s Choice
A sense of mission is what drives the centenary Estonian Association of Architects to act as a replacement agent for the institution of the state architect that is currently missing in the Estonian architectural arena. Andro Mänd, Chairman of the Association, writes about what it takes to organise cross-disciplinary collaboration, an integral part of spatial design, based on the example of site selection for Paide State High School.
What kind of relationship between a space and its surroundings would help to avoid the objectification of space—i.e., treating buildings or areas as sculptures or fully controllable objects?
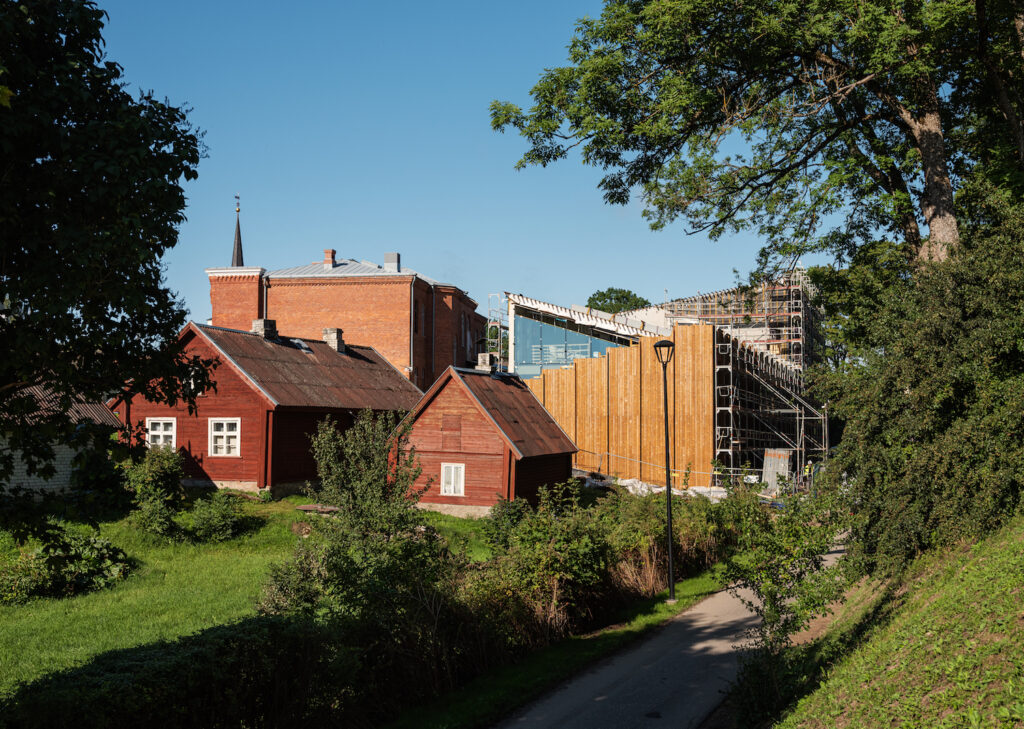
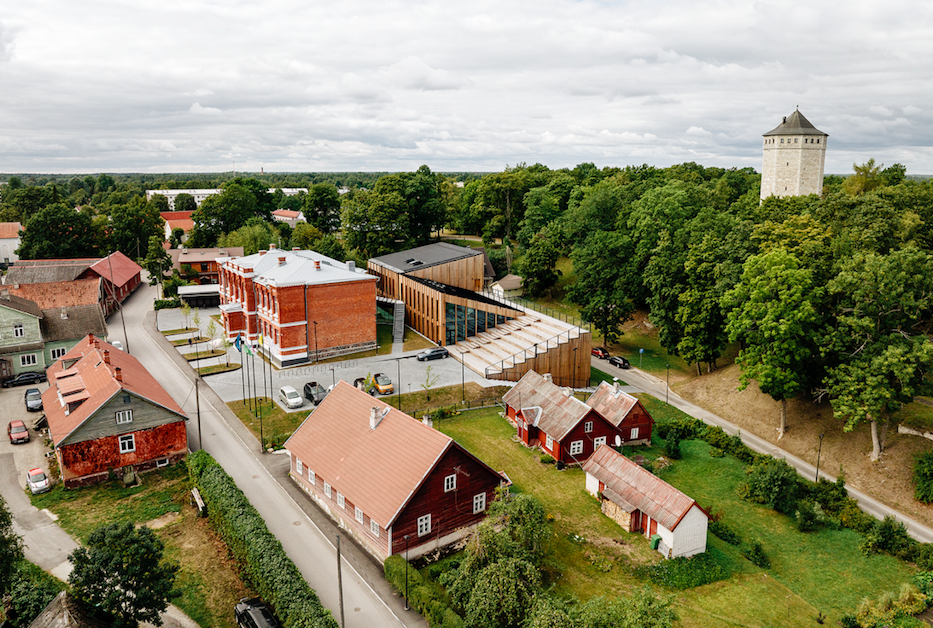
Paide State Secondary School is an excellent example of the mutually complementary dialogue between a historical space and contemporary architecture.
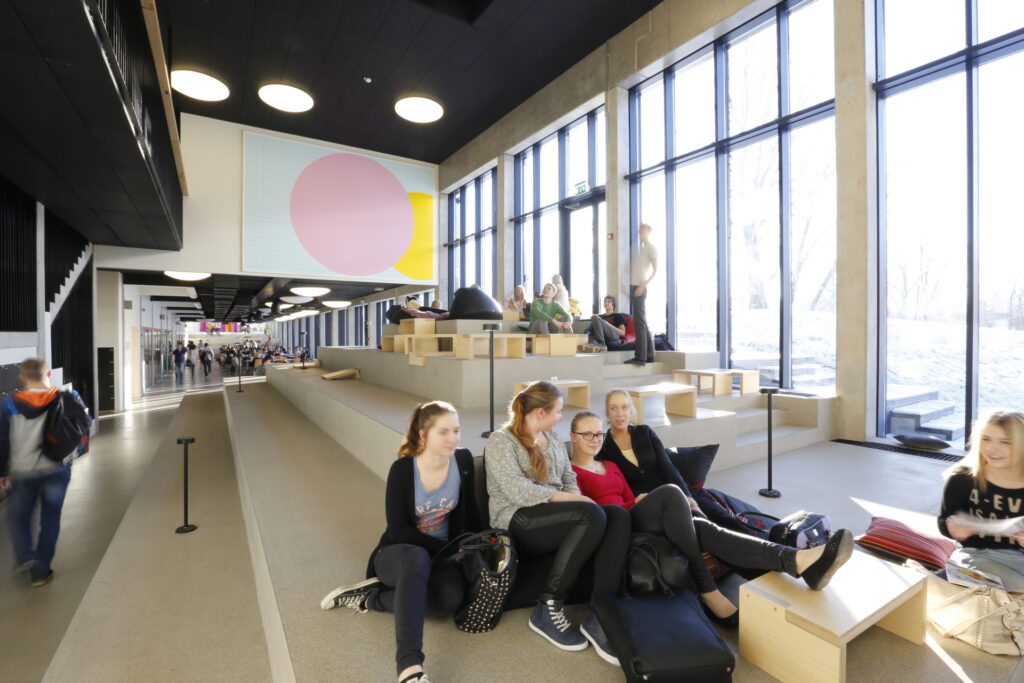
Over the course of the past thirty years, designing school spaces has migrated from being a marginally positioned subject matter to the centre of focus in the field of architecture, supported by scientific studies and continual research and development. The spaces for learning have acquired a new image and meaning.
We have gained an unprecedented amount of trust from our employers. Work has suddenly become dispersed, taking place asynchronously at different locations and different times. One gets a sense now of deeper reflection on how companies should organise their work and inspire their workers. This has led to a shift in understanding—what takes place within the environment has begun to affect the environment itself and its fundamental idea, which in turn guides the aesthetic decisions on space.
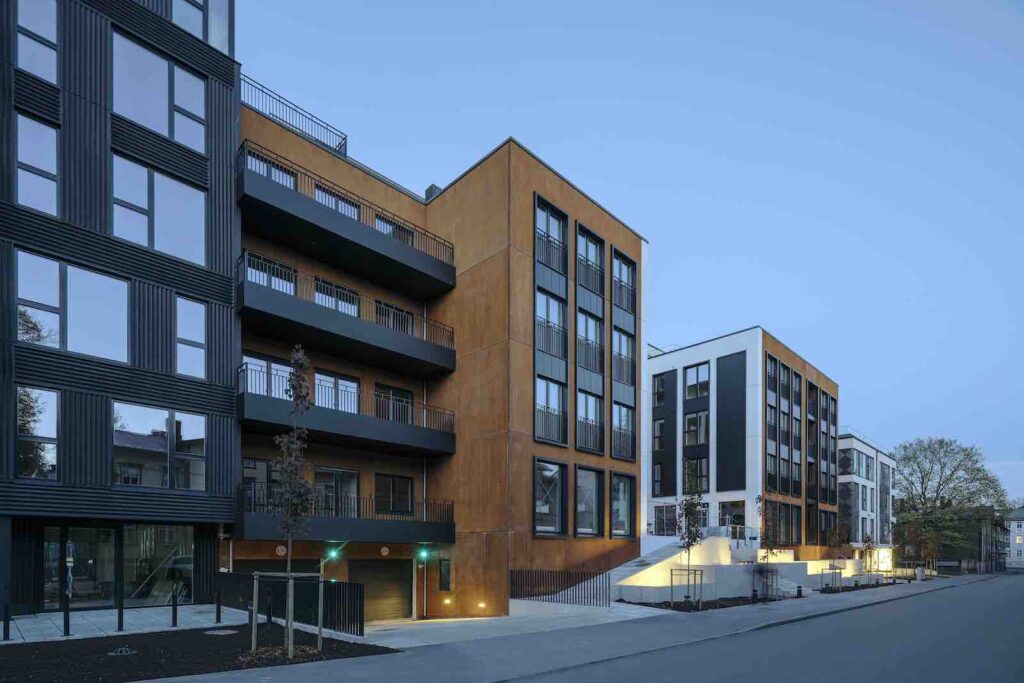
What has taken place in the field of apartment building construction over the last 30 years? Indrek Rünkla draws out some of the more significant aspects from his own personal experience.
Little was built following the re-establishment of Estonian independence in the early 1990s, however, the debates held and practices established largely came to set the foundations for the dominant issues in the architectural field in the past decades.
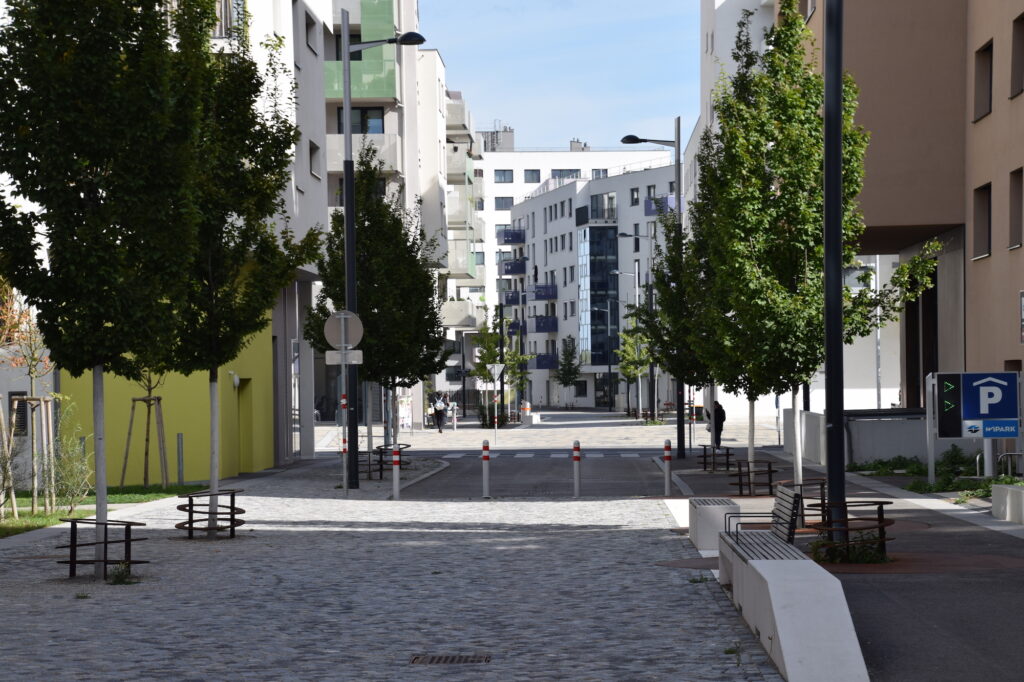
Discussions about how to plan a good city and what kind of buildings to construct are becoming increasingly relevant as mankind has reached a fundamental milestone: the majority of the society lives in cities. At the time of climate change, the issue of a sustainable city is more pressing than ever before also in Estonia, where motorisation is fast and local centres are subjected to urban sprawl. In this context, it is worth recalling the ideological principles of two urban design theories – New Urbanism and Landscape Urbanism – in order to set goals for the kind of space we want to move towards and the pitfalls to avoid on the way.
Teist põlve arhitekt Ralf väidab, et tal ei ole eriala suhtes illusioone; seda muljetavaldavama järjekindlusega seisab ta projekteerimisprotsessis arhitektuurse tuumidee säilimise eest. Arhitektiks olemine defineerib Ralfi kogu tegevust ja maailmavaadet töötegemisest reisimiseni – võib-olla ainult muusikal õnnestub hetkiti samavõrdse tähelepanu eest võistelda. Küsis Ingrid Ruudi.
Villem Tomiste is like a figure from the beginning of 20th century Young Estonia movement – genuinely European, deeply urban, and as such, slightly suspicious for the local conservative community. Unlike many architects who preach social benefits, he actually lives by what he promotes in his civic visions – urbanistically to the core, commuting on foot and by tram, avoiding over-consumption, and with a refined aesthetic sensibility. Contemporary spatial culture is, for him, a field of opportunities: extending from urban planning and landscaping projects to dialogues with contemporary music, the visual arts and various exhibition practices.
Postitused otsas